Patterns for collaborative work in healthcare

We used our rigorous framework to formally verify the correctness of anumber of collaboration patterns in healthcare teams by looking at specifications of responsibility and accountability. Particularly, we analysed two types of patient handovers, which we modelled as process compositions that were then mechanically verified. The formal underpinning of our approach provides guarantees that all the necessary information for the patient handover is communicated, while enforcing the specified conditions for responsibility and accountability in every workflow instance.
Problem
Collaboration of healthcare teams is a crucial aspect of modern hospital practice, and one of the most important issues to consider when ensuring the continuity of patient care. However, members of hospital staff tend to follow informal procedures for collaboration (e.g. during patient handovers), thus raising the following questions: Are the adopted collaboration patterns correct? Is the required information effectively communicated? How is accountability and responsibility of staff members propagated throughout the collaboration?
Our approach
We have applied our methodology for modelling, verifying and deploying healthcare workflows to answer the above questions and developed a software system that supports collaborative work in healthcare teams. The findings and results of each phase are further explained below.
Conceptualisation of collaboration processes
Focusing on healthcare collaboration scenarios that involve two actors, we investigated two patterns of collaboration: the assignment and delegation of a clinical service from one healthcare practitioner to another. We analysed these patterns by considering relevant literature and taking into account the transfer of responsibility and accountability for each case. The end result was a set of processes involved in each pattern, along with their inputs, outputs, preconditions and effects. Table 1 shows an illustrating extract of the conceptualised processes.
| Process | Input | Output |
|---|---|---|
| Service Assignment Request | No open Contracts | Assignment |
| No other Requests | Requested Healthcare Contract | |
| Healthcare Service Requester | Healthcare Service Requester | |
| Healthcare Service | Pending Healthcare Service | |
| Collaboration decision | Requested Healthcare Contract | (Accepted Healthcare Contract |
| Healthcare Service Provider) | ||
| OR | ||
| Rejected Healthcare Contract |
Formalisation of collaboration processes
We diagrammatically specified the processes for assignment and delegation with the use of our visual tool, which seamlessly devises their logical representation in the background. 1 presents an example of the graphical and logic-based representation of the process “ServiceASSGRequest”, which corresponds to the task of requesting the assignment of the clinical service to another healthcare practitioner.

Figure 1: Visual representation of the Service Assignment Request process
Collaboration patterns as processes compositions
The formally specified processes were then graphically composed into two workflows - one for assignment and one for delegation - which were mechanically verified. The workflow representation of the assignment pattern is presented in 2. The workflows obtained provide a visual account of the sequence of collaboration steps in each pattern, and make evident the transfer of responsibility and accountability. The formal foundations of our approach provide guarantees that the patterns are verified with respect to both the consistency of the information flow through the individual processes and the systematic matching of their preconditions and effects. It also makes it possible to explicitly handle exceptions and enforce additional constraints on particular parameters.
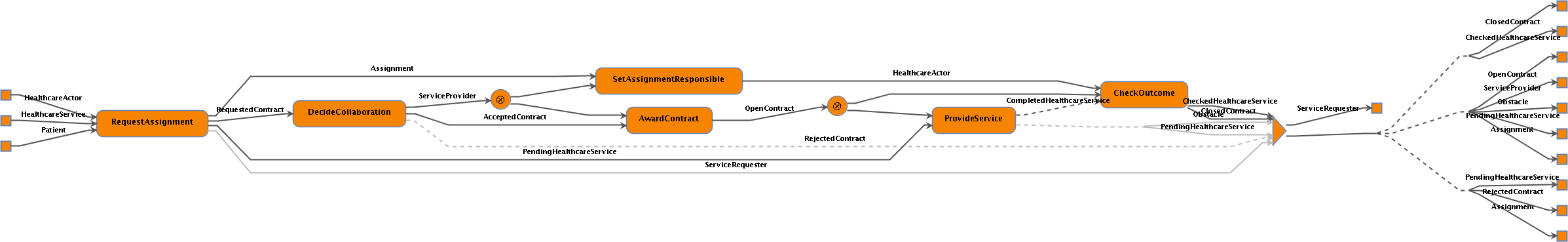
Figure 2: Composed workflow for the assignment pattern
Workflow deployment for healthcare collaboration
Utilising our systematic, automated procedure for workflow deployment, we translated the constructed workflows into a web-based information system for collaborative work in healthcare teams. This software solution allows each member of staff to view the information and actions that are relevant to them, as shown in the sample screenshot in 3. More importantly, the clinical policies defined in the design phase are automatically and formally enforced, and responsibility and accountability are tracked mechanically. The end result ensures the consistency of the information flow, enabling the effective communication between healthcare practitioners. Additionally, it is maintainable and can be easily integrated with other software solutions, such as electronic medical records.
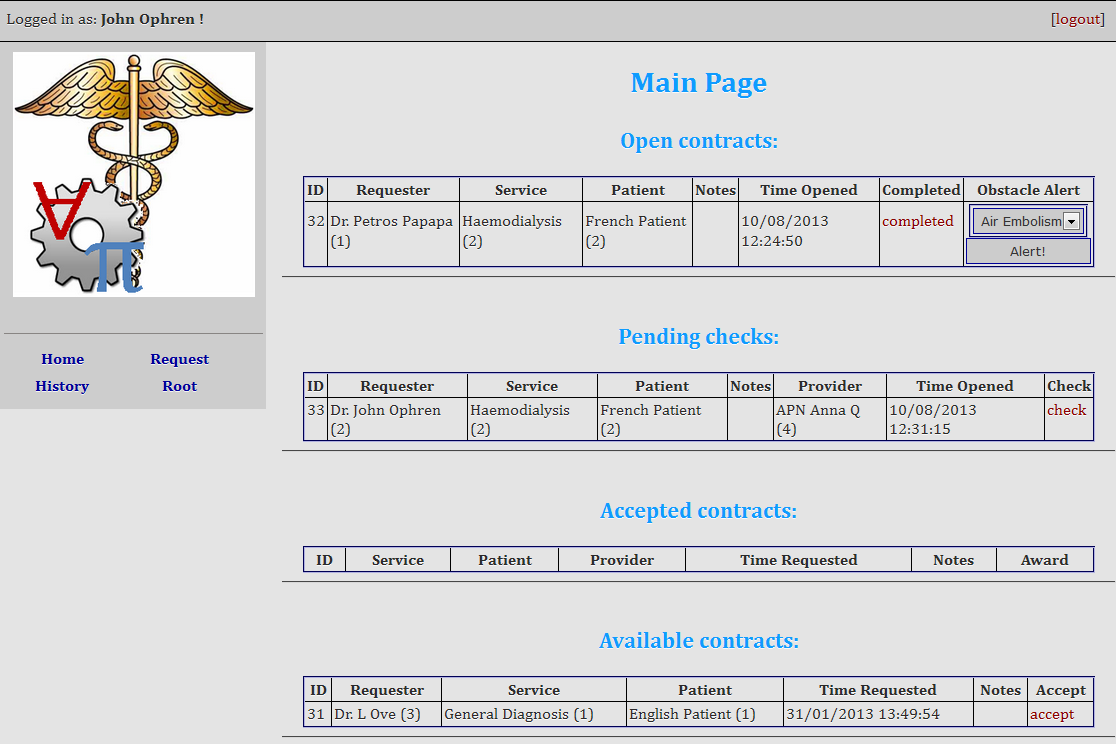
Figure 3: Software prototype for collaborative work in healthcare teams
Benefits
- guaranteed consistency of collaboration patterns
- tracked responsibility and accountability
- explicit exception handling
- automated & maintainable workflow deployment
- effective communication & verified information flow
- enforced clinical collaboration policies
- increased collaboration efficiency
